On April 25, 2024, the Biden Administration approved new rules to establish carbon capture and clean fuels guidelines, along with standards for utilities related to certain types of fossil fuel generation assets. The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) estimates that these measures will prevent 617 million metric tons of carbon pollution from existing coal and new natural gas-fired plants between 2028 and 2042. These EPA rules are part of a larger suite of regulations over the past few years aimed at creating market and technology opportunities to achieve the ambitious federal target of 100 percent clean energy by 2035.
Black & Veatch’s 2024 Electric Report — based on expert analysis of almost 700 respondents to a survey of U.S. electric stakeholders — takes the pulse of the U.S. utilities against the headwinds of change in this evolving energy ecosystem, propelled by megatrends such as decarbonization and sustainability.
Prioritizing Power Planning
At a time when utilities are examining their priorities to develop energy programs that support their endusers’ energy efficiency and initiatives to accelerate cleaner energy solutions, Black & Veatch’s latest survey distills important insights about investment priorities, decision trade-offs and drivers.
Perhaps predictably, respondents increasingly are investing in solar technologies. More than half of respondents (54 percent, up 6 percentage points from last year) categorized solar as a high investment priority when it comes to reducing greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions (Figure 11).
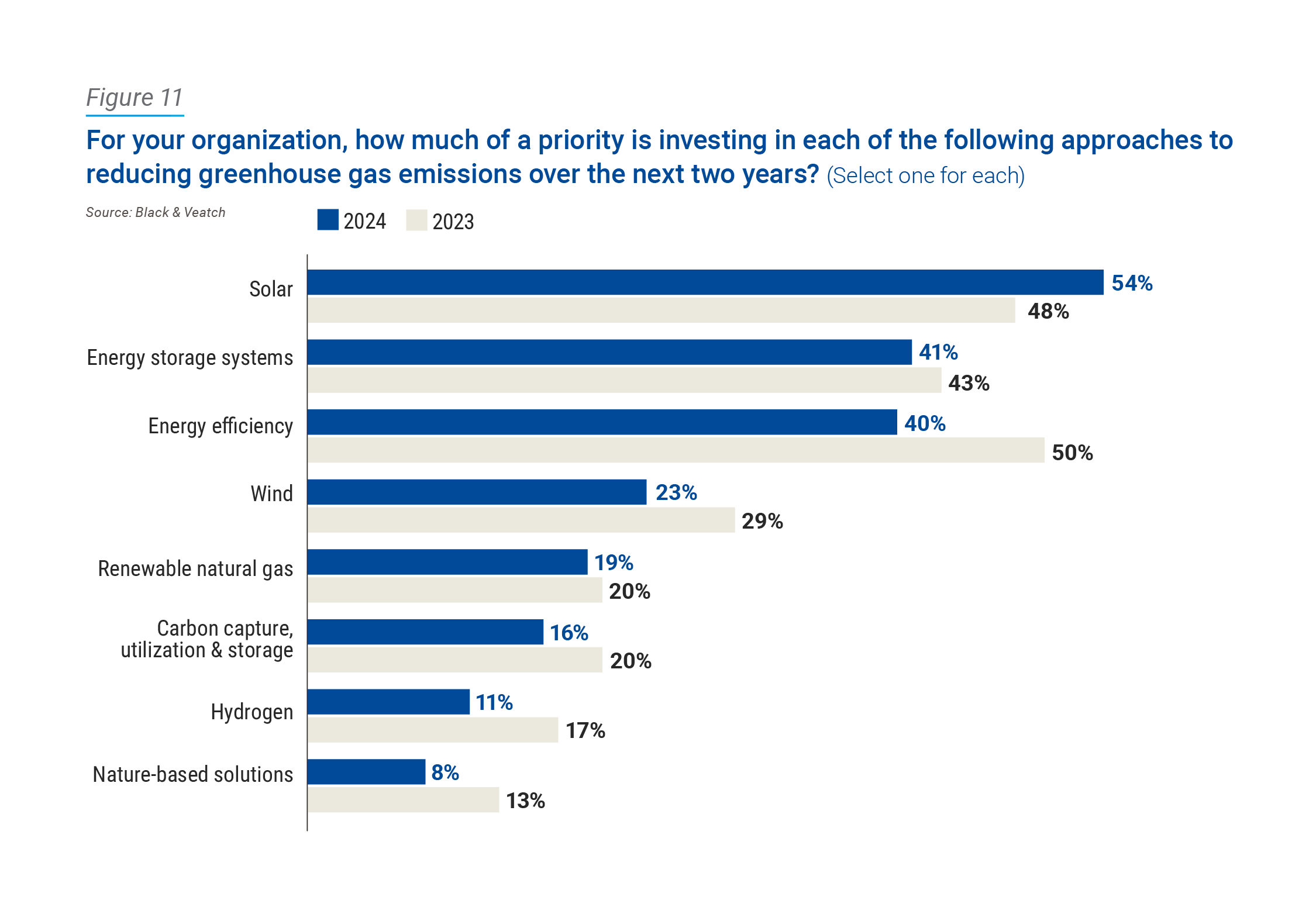
Energy storage systems jumped to second as a utility priority at 41 percent (consistent with 43 percent in 2023), passing energy efficiency, which fell to third, dropping 10 points to 40 percent. Utility demand-side management programs have been in place for decades as an important collection of incentives and solutions, but reducing, shifting or optimizing existing energy usage only allows utilities and their customers to address part of their sustainability and emissions reduction requirements.
On April 4, 2024, the EPA announced $20 billion in awards to accelerate clean energy projects across the United States, under the Greenhouse Gas Reduction Fund authorized under the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) in 2022 to offset the costs of pursuing emissions reduction projects. However, under a broader range of IRA grants, loans and tax incentives, it is challenging for utilities (and private companies) to have clarity about eligibility and the overall potential impact on project economics, which could result in some utilities temporarily holding off on prioritizing investments in renewable natural gas, hydrogen or wind or solar-based solutions until the pathways to funding are clearer.
In a crucial time for the energy transition, integrating supply-side and demand-side energy resources, as well as stacking multiple technologies to determine the net effect in reaching decarbonization goals, is more challenging than ever. The Pew Research Center finds that most Americans support developing alternate energy sources. It follows that utilities are valuing as their highest priority the use of solar — a widely accepted, proven energy source.
Reality Versus Perception
In an election year, it’s easy for a politician to speak about their vision for America’s future, but what about the reality of it all? Is 100 percent clean energy by 2035 even feasible? With only about a decade left until this goal, the pressure is on.
So, what’s the roadmap? What trends most intrigue U.S. electric sector stakeholders? Respondents weighed in, citing new grant and loan opportunities to help offset costs (45 percent) as the top trend in which they’re most interested. Around-the-clock, firm dispatchable power from renewable resources and storage drew 41 percent, followed by clean energy tax credits (41 percent) (Figure 12). A takeaway: when two of the top three responses revolve around funding to aid utilities in decarbonization, the energy transition’s fate really may come down to money.
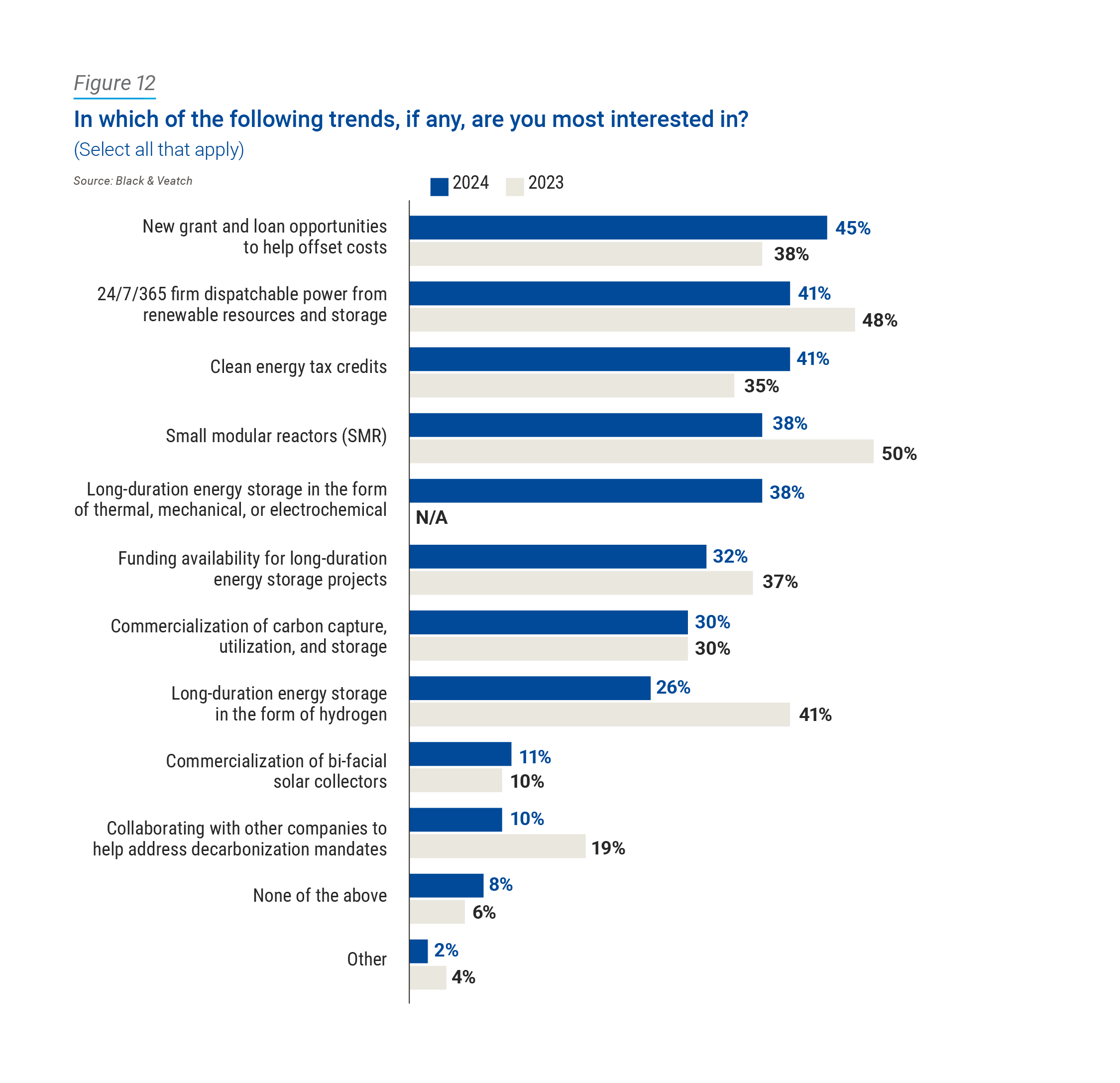
At least year over year, small modular reactors (38 percent, down 12 percentage points from 2023) and long-duration energy storage involving hydrogen (26 percent, down from 41 percent) had the sharpest declines among respondents. For hydrogen energy storage, high supporting infrastructure costs and/or geologic siting requirements associated with this solution could be a driving factor in the decline. Hydrogen is difficult to move around and is one of the least efficient fuel sources when created via electrolysis from renewable sources. The deployment of hydrogen hubs that include production, storage, distribution and transportation of hydrogen could spark renewed utility interest in utilizing hydrogen for energy storage as a part of their strategy.
Energy Storage Needs
As decarbonization plans are refined annually and the energy transition becomes more of a reality for utilities, so does the need for energy storage. Not only are utilities generating different forms of energy such as solar or wind, but the intermittent nature of renewable energy requires reliable and widespread energy storage.
According to respondents, almost two-thirds (64 percent) note that they need energy storage, but no more than one week’s worth, while only 6 percent report needing it for longer than a week. Since long-duration energy storage is classified as 12 hours or more, 41 percent are looking at long-duration use cases. Meanwhile, almost one-third (30 percent) report that they need less than 12 hours of energy storage. (Figure 13).
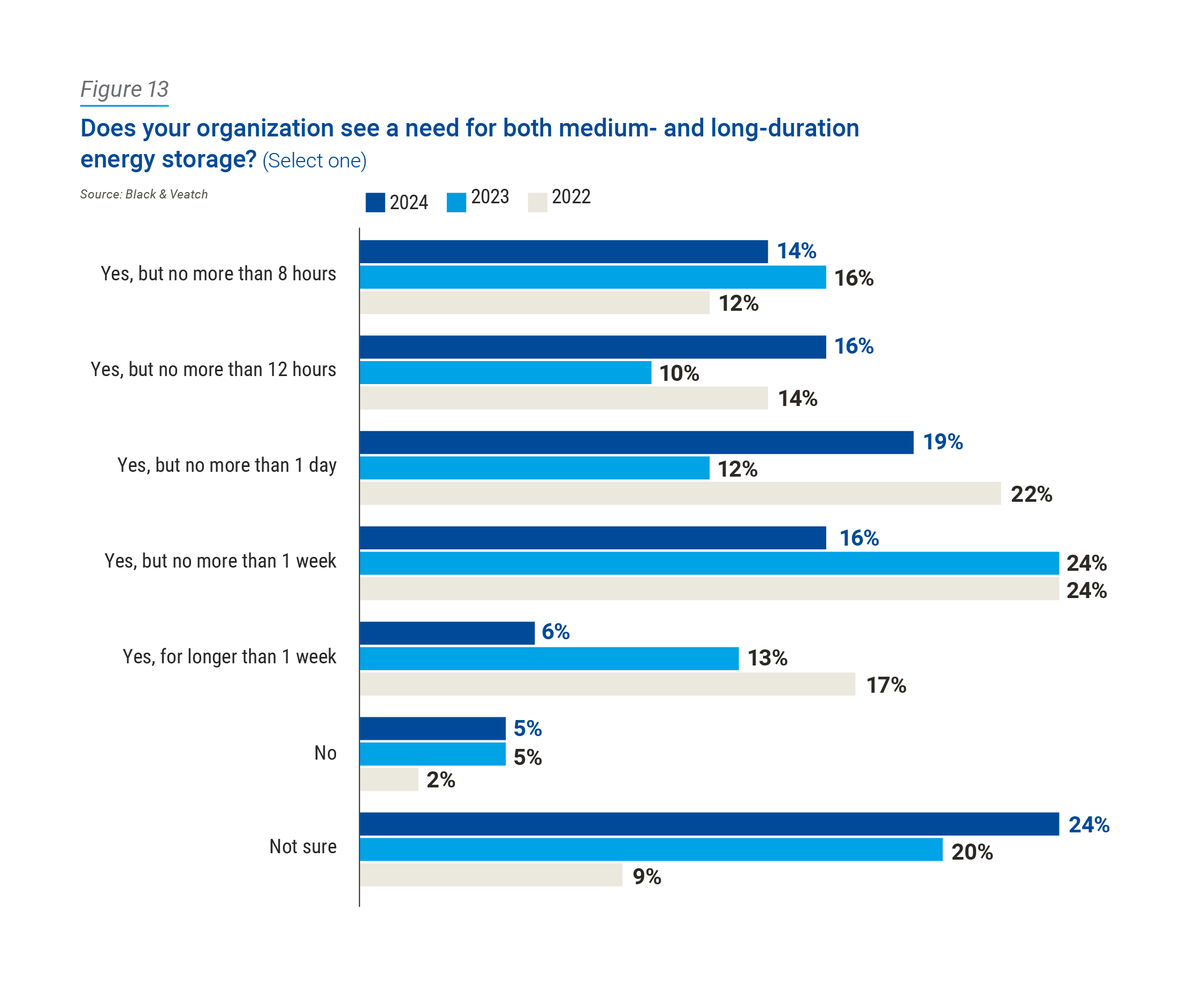
To better understand this data, it’s important to understand what assets or functions the respondents are planning to replace with energy storage. As an example, to fully support solar with energy storage alone, the utility would need to replace the hours of the day that the sun doesn’t shine with enough storage to fill in the nighttime capacity gap plus additional storage for low production days. On top of that, it is crucial to maintain the storage that could provide grid stability for voltage swings caused by intermittency of these systems. Respondents could be looking at medium- (12 hours or less) or long- (12 hours or more) duration energy storage for all these needs, or only a part.
As the responses shift year to year — with the most notable change being a drop from 24 percent in both 2022 and 2023 to only 16 percent now in terms of needing no more than one week of energy storage — this could mean a variety of things. It could represent refinement in decarbonization plans as emerging technologies become more or less viable as commercial options. Another factor in storage duration difference is likely the maturity of the respondent’s plan. If a utility is still working on the first couple of phases of their plan, they likely don’t have as great a need for long duration energy storage yet.
Money and regulatory requirements are the driving force behind the pursuits around cleaner energy, with a critical element being the timing of funding incentives and regulations that would force compliance. Nearly one-third of respondents — 32 percent — cited a need for funding for long-duration energy storage projects as a trend of interest.
When all signs point back to funding, the message is loud and clear. Is the future of the energy transition dependent on consistent, reliable funding? That might just be so. With funding expected to accelerate in the next 12 to 18 months, this picture may look different, and the perception of what the energy industry could look like might start to meet reality.







